Analysing the various elements of a job-to-be-done is at the core of the Customer-Action Cycle model. Human behaviour is an aggregation of multiple actions, and value can be discovered by studying these actions. The unit of analysis is customer action. The CAC model addresses the question: “Where can we look for customer value and How to find it?”
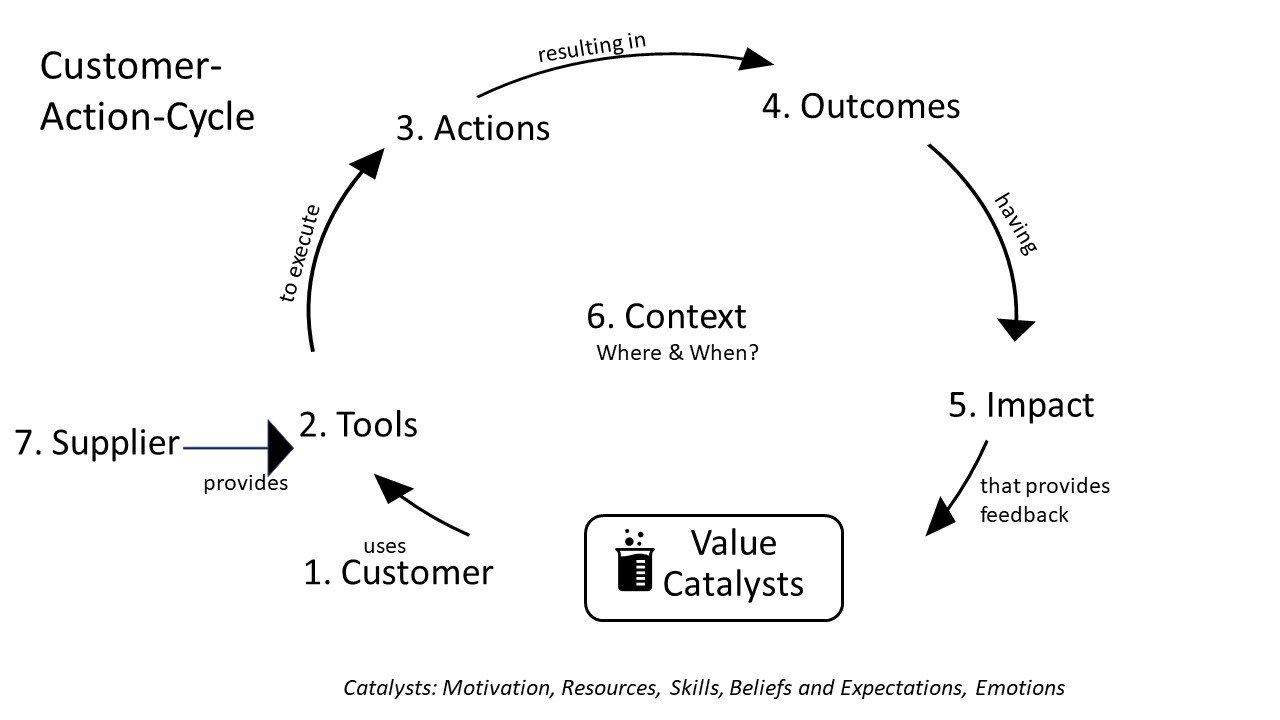
The CAC model is simple and at the same time captures all the elements associated with discovering value in an elegant and logical way. The relationship between the value nodes is represented by verbs. The sum of all these relationships constitutes the overall customer experience. It may be noted that the supplier value node is outside the Customer-Action Cycle but contributes to customer value. If the customer has a choice of multiple offerings that provide similar value, the differentiating factor that is likely to influence the customer’s decision is supplier perception and relationships.
Criteria that help evaluate the contribution of a node or a catalyst to customer value are called value criteria. These criteria are standard characteristics that will be the same across domains, products, or services. Each of these criteria can be broken down into attributes that are specific to the customer’s circumstances. For example, product features, design, availability, promotional offers, usability, ownership, performance, quality, and price are some of the standard value criteria associated with the node called tool. All the CAC model elements are interconnected, and any change in one element will impact other components of the model.
According to the Customer-Action-Cycle model, customer value resides in the value nodes, value catalysts and in the overall customer experiences that define the relationship between the customer and the elements of the model.
High levels of motivation, enabling beliefs, relevant skills, appropriate resources, and resourceful emotions play an important role in influencing customer decisions and realising value. These are the value catalysts that can help customers make decisions.
To understand how the CAC model works, the reader can go through this example





